- Standard Logging
(Intermediate surveys) are carried out after completion of intervals drilling scheduled for overlapping by the conductor, intermediate column(s), as well as the production column above the first productive or promising interval, to assess the spatial position and wellbore integrity for safe drilling.
- Final Logging
The final logging in all wells is performed in productive and promising oil and gas intervals, in conjunction with materials from other survey types.
TASKS HANDLED:
-
Dismembering the section under survey into formations up to a thickness of 0.4 m, binding of formations along well depths and absolute elevations;
-
Detailed lithological describing of each formation, marking all type reservoirs (porous, fractured, cavernous and mixed) and determining their parameters – clay content coefficients, total and effective porosity, permeability, water, oil and gas saturation (if reservoir effective thickness exceeds 0,8 m);
-
Separating reservoirs by the nature of their saturation into productive and aquifers, and the productive ones into gas and oil-saturated;
-
Determining the positions of fluid-fluid contacts, boundaries of transition zones, effective gas and oil saturation thicknesses;
-
Determining reservoir pressures and temperatures;
-
Determining mineralization of formation waters;
-
Forecasting of potential production rates;
-
Forecasting of the structure of the geological cross-section in the near-wellbore and interwell spaces.
-
Determining the spatial position of the wellbore along the zenith and azimuth angle (directional survey) and matching the well path to project data;
-
Determining the average well diameter (caliper logging) and the cross-sectional profile of the borehole in two orthogonal planes (profile logging), marking key seats, cavities, packings, cuttings and mud cakes against these data;
-
Measuring temperature and its vertical gradient in drilled and idle wells.
-
Detection of gas, oil, water contacts.
-
Monitoring the survey process and determining formation hydrodynamic and process characteristics.
Acoustic Cement-bond Logging
- Designed to determine the height of the cement mix reached, the degree of filling the annulus with cement and its adhesion to the casing and rocks, the presence of the expanded (gas-saturated) cement in the cement of the vertical channels and the intervals.
- Acoustic cement-bond logging is based upon measuring the characteristics of wave packets propagating in the column, cement stone and rocks. Informative characteristics are the amplitude or coefficient of the effective wave along the column, as well as the interval time of propagation of the longitudinal wave. Phase correlation diagrams are used to estimate the cement-bond at a quality level. The vertical resolution of the method is 40 cm, the horizontal resolution is 40 cm. It is used in cased wells filled with free-of-gas liquid based on oil or water.
TASKS HANDLED:
- Determining the height of the cement reached;
- Assessing the state of contact of a plug-back mixture with the casing string and rocks;
- Assessing annulus integrity.
Methods Applied for Well Construction:
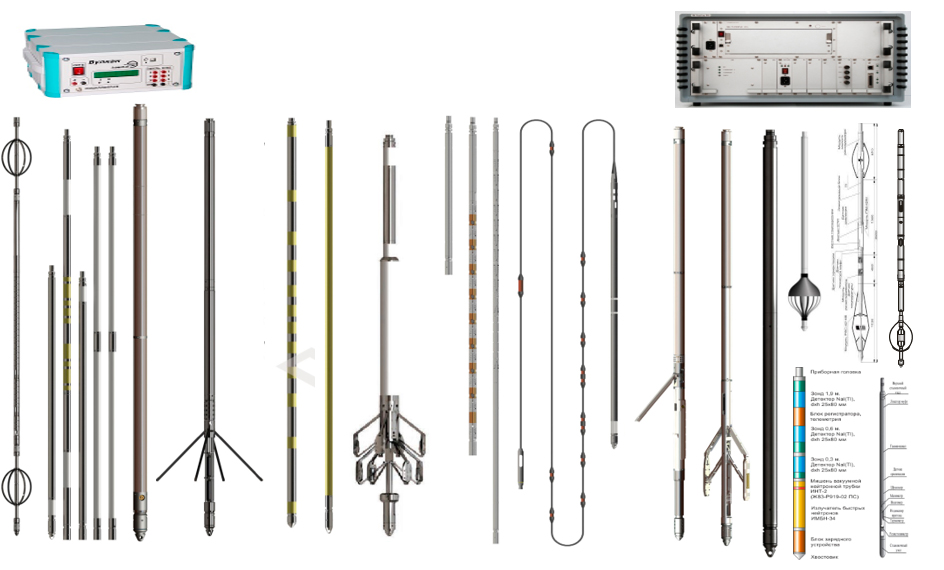
- Electrical logging (methods: apparent resistance (AR), self-polarization potential (SP), resistivity logging, lateral multi-probe logging (LL), lateral probe logging (LPL), micrologging (ML), induction logging (IL), high-frequency induction isoparametric probe logging (VIKIZ), micrologging scanning (MS);
- Radioactive logging (methods: gamma logging (GL), neutron gamma logging (NGL), variations of neutron-neutron logging (NNL), density gamma-gamma logging (DGGL), litho-density gamma-gamma logging (LDGGL), spectrometric gamma-ray logging (SGL);
- Acoustic logging (methods: acoustic logging (AL), acoustic cement-bond logging (ACL), acoustic intergral scanning (AIS), acoustic multisector logging, acoustic broadband logging (ABL);
- Directional survey;
- Caliper logging, profile logging
; - Temperature logging
Horizontal Open Hole Well Surveys:
- Horizontal wells are surveyed by autonomous geophysical instruments that are designed to carry out a standard set of well geophysical surveys in an autonomous mode by running geophysical instruments into directional and horizontal wells on drill pipes.
- Small-sized devices are used with drilling fluid flushing and the possibility of retrieving the devices from the containers through a drilling tool if an accident. The system can work both on accumulator batteries and dry batteries, depending on the required temperature range in the borehole
- Logging on drill pipes minimize the accident rate of works.
- AMK HORIZONT instrumentation complex is used when logging in directional and horizontal wells.